- By Coursera Staff
- 28 Aug 2022
UI vs. UX Design: What’s the Difference?
Introduction
- User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) are terms frequently used in tech circles, often interchangeably. However, they have distinct meanings.
- This article aims to clarify the differences between UX and UI designers' roles, how to choose which one to pursue, and how to get started even without a degree or prior experience.
Difference between UI and UX
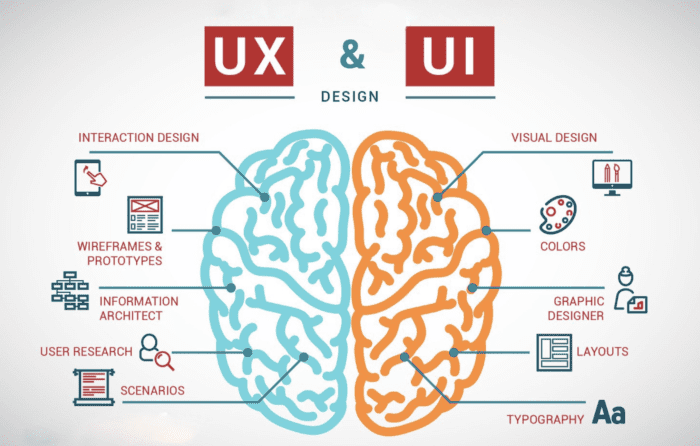
- User Interface (UI): Refers to the screens, buttons, toggles, icons, and other visual elements you interact with when using a website, app, or electronic device.
- User Experience (UX): Encompasses the overall interaction you have with a product, including your feelings about that interaction. While UI can influence UX, they are distinct, as are the roles of designers.
Examples
- A banking app may look great and have intuitive navigation (UI), but if it loads slowly or requires many clicks to transfer money (UX), users will have a poor experience.
- A website with unique, helpful content organized logically but looks outdated or is hard to navigate will likely lose users.
Tasks and Responsibilities of Designers
UX Designers
- Focus on the experience users have with a product, aiming to make products functional, accessible, and enjoyable.
- Common tasks:
- Conducting user research to identify goals, needs, behaviors, and pain points.
- Developing user personas based on target customers.
- Creating user journey maps to analyze customer interaction with the product.
- Building wireframes and prototypes.
- Performing user testing to validate design decisions and identify problems.
- Collaborating with stakeholders, UI designers, and developers.
UI Designers
- Create the graphical portions of mobile apps, websites, and devices.
- Common tasks:
- Organizing page layouts.
- Choosing color palettes and fonts.
- Designing interactive elements like buttons, menus, and text fields.
- Making high-fidelity wireframes and layouts.
- Working closely with developers to convert designs into a functional product.
Is There Such a Thing as a UI/UX Designer?
- Some companies look for UI/UX designers, but often the role leans more towards one than the other.
- Pay more attention to the list of tasks or qualifications rather than the job title itself.
Skills
- UX Skills: Product strategy, user research, information architecture, testing, and iteration.
- UI Skills: Color theory, typography, design patterns, interactivity, and animation.
- Shared Skills: Empathy, collaboration, design thinking, prototyping.
Education
- A degree isn't always necessary to get a job as a UX or UI designer, but it can open up new opportunities.
- UX designers might have degrees in computer science, psychology, human-computer interaction, or design.
- UI designers might have degrees in digital design, graphic design, or interaction design.
How to Choose Between UI and UX?
- Both UI and UX design are well-paying careers in demand. Your choice depends on your goals and interests:
- If you are interested in technology, enjoy variety, and love problem-solving, UX design might be a good fit.
- If you are a creative thinker with a strong aesthetic sense, consider UI design.
Tips to Decide
- Take a class in each field to experience them firsthand.
- Read or listen to popular UI/UX blogs and podcasts to learn from experts.
- Reach out to industry professionals for informational interviews.
- Join online design communities to ask questions.
Other User Experience Roles
- UX Researchers: Study the goals, needs, wants, and pain points of users.
- UX Writers: Write the text that appears on websites, apps, and other digital products.
- Interaction Designers: Focus on how users interact with digital products holistically.
- Developers: Convert designs from UI and UX designers into usable software, websites, or applications.
- Product Designers: Lead the entire process of bringing a product or service from idea to reality.
- Content Strategists: Oversee the planning and production of marketing content throughout a project’s lifecycle.
Building Your UX Design Career
- You don't have to choose between UI and UX; strengthening both skillsets makes you a well-rounded designer.
- Suggested courses:
- Google’s course: "Build Dynamic User Interfaces (UI) for Websites."
- Guided project: "User Interface (UI) Design with Wireframes in Miro."
- CalArts' UI/UX Design Specialization: A comprehensive four-course series covering all stages of UI and UX development.
Conclusion
By understanding the difference between UI and UX design, you can decide which career path suits you best and develop the necessary skills to succeed in this exciting and in-demand field.